Prerequisites for Geocoding
We will start with a very basic txt file which has one attribute “name” and two fields for the address “str_num” and “code_place”. You can download the file with one “wrong” address (a common problem!) here. My goal is to create a shapefile with all rows and some nice points on my map:
As we don’t use the build-in geocoder but something from the Python world you need to download the geopy package here, extract the package using your archive software like 7-zip, winzip or whatever and place the geopy folder in your Python site package folder of your ArcGIS Python installation. The geopy-folder in the downloaded package:
The Geocoding/Shapefile Creation
First of all, we need to know how to read the csv file. Python comes with native csv support and you can read and print information out of a csv like this using the python interface in ArcGIS:
import csv
with open('C:\\Users\\ricckli\\Documents\\wd_gis\\geocoding\\adresses.txt', 'rb') as csvfile:
content = csv.DictReader(csvfile, delimiter='\t')
for row in content:
print row
The variable row has now three attributes stored. In the first the name, second and third information belongs to the address. Now we need to find out, how to geocode an address using geopy. We can simply use the information from the geopy github page and apply it to our example:
from geopy.geocoders import Nominatim
geolocator = Nominatim()
result = geolocator.geocode("1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Washington") #white house address
Once we know, how to iterate over the file and we know how to geocode an address, we can copy each row into our created shapefile (thanks to perrygeo):
import csv
from geopy.geocoders import Nominatim
geolocator = Nominatim()
cursor = arcpy.InsertCursor("Universities") #the shapefile is already part of my ArcGIS project
with open('C:\\Users\\ricckli\\Documents\\wd_gis\\geocoding\\adresses.txt', 'rb') as csvfile:
content = csv.DictReader(csvfile, delimiter='\t')
for row in content:
feature = cursor.newRow() #this is the current object we work on.
vertex = arcpy.CreateObject("Point")
vertex.X = geolocator.geocode(row["str_num"].decode('utf-8') + row["code_place"].decode('utf-8')).longitude #I am using .decode('utf-8') just to handle the umlaut problem in German names ;-)
vertex.Y = geolocator.geocode(row["str_num"].decode('utf-8') + row["code_place"].decode('utf-8')).latitude
feature.shape = vertex
feature.Name = row["name"]
cursor.insertRow(feature)
del cursor
In the end the shapefile should hold all the information of the csv we have used. Now let’s zoom to the create shapefile:
dataframe = arcpy.mapping.ListDataFrames(arcpy.mapping.MapDocument('current'))[0]
geocodelayer = arcpy.mapping.ListLayers(arcpy.mapping.MapDocument('current'), 'universities', dataframe)[0]
layer_extent = geocodelayer.getExtent()
dataframe.extent = layer_extent
Hint: Sometimes the geocoder fails. Let’s create a csv with the rows which where not succesful in geocoding by using this enhanced script:
import geopy
import csv
from geopy.geocoders import Nominatim
geolocator = Nominatim()
cursor = arcpy.InsertCursor("Universities")
failed_text =""
numbers_failed = 0
with open('C:\\Users\\ricckli\\Documents\\wd_gis\\geocoding\\failed_codes.txt', 'w') as file:
with open('C:\\Users\\ricckli\\Documents\\wd_gis\\geocoding\\adresses.txt', 'rb') as csvfile:
content = csv.DictReader(csvfile, delimiter='\t')
for row in content:
feature = cursor.newRow()
vertex = arcpy.CreateObject("Point")
coord = geolocator.geocode(row["str_num"].decode('utf-8') + row["code_place"].decode('utf-8'))
if coord is None:
failed_text += row["name"] + row["str_num"] + row["code_place"]
numbers_failed += 1
if coord is not None:
vertex.X = geolocator.geocode(row["str_num"].decode('utf-8') + row["code_place"].decode('utf-8')).longitude
vertex.Y = geolocator.geocode(row["str_num"].decode('utf-8') + row["code_place"].decode('utf-8')).latitude
feature.shape = vertex
feature.Name = row["name"]
cursor.insertRow(feature)
file.write(failed_text)
file.close()
del cursor
print "failed geocodes: " + str(numbers_failed) + "!!! check the file C:/Users/ricckli/Documents/wd_gis/geocoding/failed_codes.txt"
dataframe = arcpy.mapping.ListDataFrames(arcpy.mapping.MapDocument('current'))[0]
geocodelayer = arcpy.mapping.ListLayers(arcpy.mapping.MapDocument('current'), 'universities', dataframe)[0]
layer_extent = geocodelayer.getExtent()
dataframe.extent = layer_extent
The whole script can be downloaded. Please adjust your filenames and drop us a comment if you know another solution/enhancement!
Please also notice the usage policies of the geocoders. Like this here for the used Nominatim coder.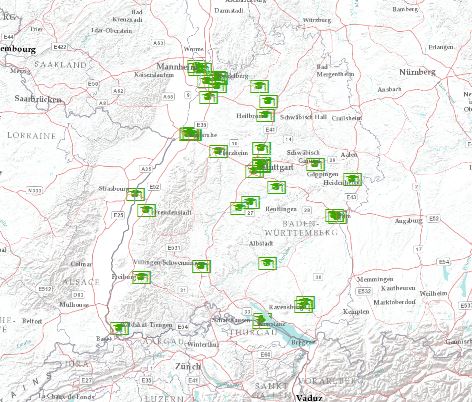
If you want to use the Google Geocoder please use the following two lines in the beginning:
from geopy.geocoders import GoogleV3
geolocator = GoogleV3()
and check the user license agreement of the Google geocoding service
I get this error
Runtime error
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “”, line 10, in
KeyError: ‘Street’
Here ‘Street’ is the name of my field header (in both shapefile table and text file) which stores the street name and house number
Ok managed to solve this. But now the script runs but nothing really happens. There are no features added to my shapefile. By the way I am running the script on only a single feature for testing. So one point must be added. But doesnt work right now.
I managed it but there is no geocoding, arc gis only displays one point out of theese 42 points
But my feature gets this 42 points