Installation
God- I am atheist, so take this not too serious- I love “pip“:pip install folium pip install pandasAnd that’s it. Just type this in your console/cmd and pip will install the module as well as dependencies for your python installation. Maybe use a super user for installing. But still very easy!
A Small Example
When it comes to webmaps you want to show some data and not only a basemap like google maps ore HERE… I would like to have a look at the median age of the population of the US states. Therefore I downloaded the US state data from the 2010 US census and converted it to a simplified, EPSG:4326 geojson and also altered/removed some columns (download it here) As known by leaflet and openlayers we will start with a basemap to put our data on and save this minimal map to a html file:import folium mapOBJ = folium.Map(location=[39.5, -98.35], zoom_start=4, tiles='Stamen Terrain') #which is the center of the us with zoomlevel 4 mapOBJ.create_map(path='map.html')Currently it seems like folium only supports the following basemaps:
- OpenStreetMap
- Stamen Terrain
- Stamen Toner
- Mapbox Bright
- some mapquest
- CartoDB Dark Matter
- some more…
The framework behind it is leaflet so you can easily enhance it with some leaflet/JS superpowers. Now let us add the geojson which is a simple one-liner:
import folium mapOBJ = folium.Map(location=[39.5, -98.35], zoom_start=4, tiles='Stamen Terrain') #which is the center of the us with zoomlevel 4 mapOBJ.geo_json(geo_path='pop_us_simple.geojson') mapOBJ.create_map(path='map.html')At the moment the shapes of the geojson is plotted on the webmap. Now let’s combine this with some data. This get’s a bit ugly as we are coming from the geojson side which is a nested json and we don’t use plain jsons. The idea in folium is: join the shapes with additional information:
import folium, json
import pandas as pd #we will use this to store the properties-data in a "pandas" data frame
mapOBJ = folium.Map(location=[39.5, -98.35], zoom_start=4, tiles='Stamen Terrain') #which is the center of the us with zoomlevel 4 and a custom attribution
with open("pop_us_simple.geojson") as file: #first read the file and store it in an object
data = json.load(file)
data2 = pd.read_json(json.dumps(data["features"]), typ='frame') #now convert it to a pandas data frame
data2 = data2.ix[:,1] # we select only "properties" as we don't care about geometry and stuff.
data2 = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame.from_dict(item, orient='index').T for item in data2]) #each item in data2 is a dict. data2 has only one column with a dict. so we "slice" the dict into several columns.
mapOBJ.geo_json(geo_path='pop_us_simple.geojson', data=data2, columns=['STUSPS10', 'median_age'],key_on='feature.properties.STUSPS10',fill_color='YlGn', fill_opacity=0.7, line_opacity=0.2) #this will add the geo from the geojson and connect it with the data in the object data2. "key_on" and first entry in "columns" must match. fill_color is from colorbrewer.
mapOBJ.create_map(path='map_median_age.html')
This is now a nice map:We can also add some points to this. So let us add some markers for cities (file is here) and create a popup filled with data:
import folium, json
import pandas as pd #we will use this to store the properties-data in a "pandas" data frame
mapOBJ = folium.Map(location=[39.5, -98.35], zoom_start=4, tiles='Stamen Terrain') #which is the center of the us with zoomlevel 4 and a custom attribution
with open("pop_us_simple.geojson") as file: #first read the file and store it in an object
data = json.load(file)
data2 = pd.read_json(json.dumps(data["features"]), typ='frame') #now convert it to a pandas data frame
data2 = data2.ix[:,1] # we select only "properties" as we don't care about geometry and stuff.
data2 = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame.from_dict(item, orient='index').T for item in data2]) #each item in data2 is a dict. data2 has only one column with a dict. so we "slice" the dict into several columns.
mapOBJ.geo_json(geo_path='pop_us_simple.geojson', data=data2, columns=['STUSPS10', 'median_age'],key_on='feature.properties.STUSPS10',fill_color='YlGn', fill_opacity=0.7, line_opacity=0.2) #this will add the geo from the geojson and connect it with the data in the object data2. "key_on" and first entry in "columns" must match. fill_color is from colorbrewer.
with open("places.geojson") as file:
cities = json.load(file)
for city in cities["features"]:
mapOBJ.circle_marker(location = [city["geometry"]["coordinates"][1],city["geometry"]["coordinates"][0]], radius=200,popup="Name: " + city["properties"]["name"]+ " (Population: "+ str(city["properties"]["pop_max"]) + ")")
mapOBJ.create_map(path='map_geojson.html')
This will create a map with geojson states and single markers with popups.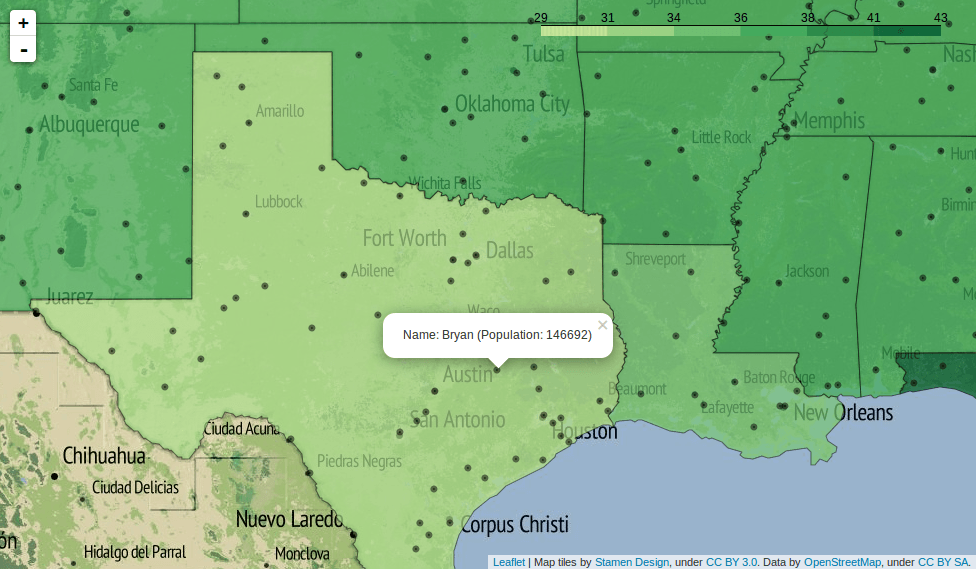
Many thanks for the short example. This just comes handy… 😀